 PANELISTS: ANISH GUPTA, CHAITANYA MANDUGULA, JIVRAJ KARWA, MIHIR KULKARNI, SANDEEP UPADHYAY, SHARTH MADAN, SHREERANG JAVADEKAR, VAIBHAV BHOSAL
PANELISTS: ANISH GUPTA, CHAITANYA MANDUGULA, JIVRAJ KARWA, MIHIR KULKARNI, SANDEEP UPADHYAY, SHARTH MADAN, SHREERANG JAVADEKAR, VAIBHAV BHOSAL
Water is a precious resource. Even today, large parts of India face the problem of water scarcity. By virtue of its proximity to Powai lake, IIT Bombay is blessed in that regard.
Here, we delve into the matter of water supply and usage on campus. The huge disparity between water consumption levels in insti and the rest of Mumbai shows a callous approach towards water as a resource. We also look into the ways water is being wasted and reasons thereof.
Background

The water supply network of IIT Bombay is very complex, and has degenerated into dilapidation over the years, since its laying down in 1960s. The primary source of drinking water is the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) pipeline, which supplies water to the campus 24 hours a day. The Tulsi and Tansa lakes are its primary sources.
The one and only water meter of the campus is installed on this line, and it caters to two main tanks located near Hostel 15. These have capacities of four and six lakh litres respectively.There are a total of 24 borewells (secondary sources) on campus catering to gardening, flushing and water-intensive laboratories such as the Hydraulics Lab.
As estimated from estate office data, the average litres of water consumed per person per day (LCPD) in the institute is approximately 358 litres. CPHEEO (Central Public Health and Environmental Engineering Organization) norms recommend the usage of water in residential areas of metropolitan cities such as Mumbai to be 150 lcpd and 45 lcpd for offices. Clearly, IITB‘s consumption exceeds CPHEEO norms by a jaw-dropping amount.
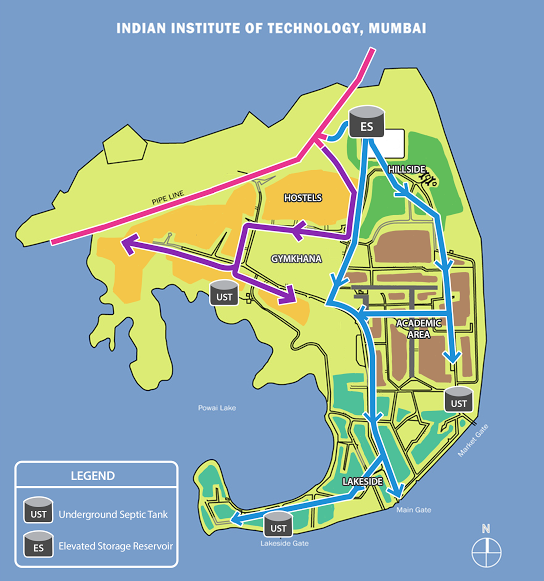
Heat map of the IIT-B water supply
The current infrastructure is getting old and has already outgrown the capacity for which it was designed. The ever-increasing population in the institute has led to increasing pressure on the supply system, which operates pumps for 24 hours – an inefficient modus operandi.
It has been noticed that the meter on the high pressure BMC pipeline gets damaged every few months due to flowing debris. Given that around 20-25 days are needed to fix it, measurements, and subsequently, water bills, for that period are merely an approximation of previous months’ records.
While many recent changes have been made to the pipeline system, necessary documentation which could be used at the time of repairing is still missing. Often, senior officials at the estate office are called to address the problem whenever a complaint is registered, which increases response time.
Case Studies
Comparing consumption on campus with any established norm is hard because it cannot be put in one category. Also, the absence of meters means that the figure of 358 lcpd cannot be subdivided on types of usage. However, to gather information about consumption patterns across the institute, approximate calculations were made using pipeline diameters and capacities of storage tanks.
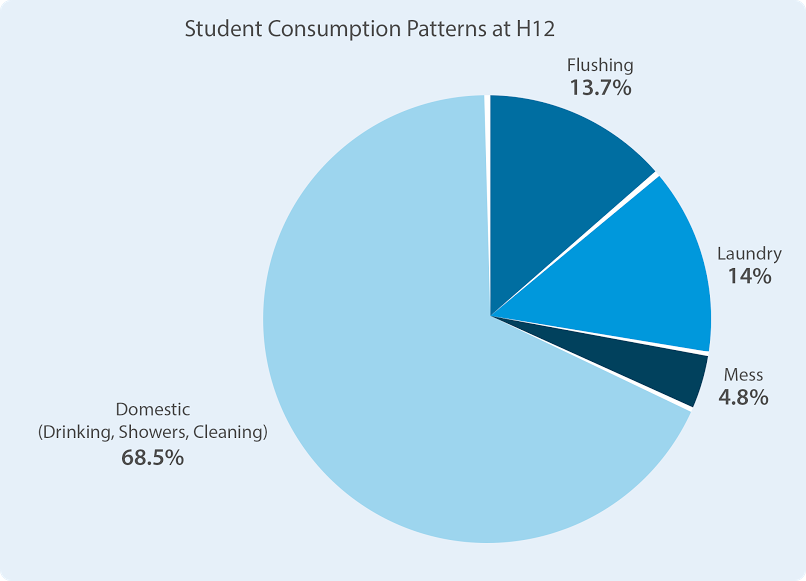
Although corrective steps have been taken by introducing wastewater recycling systems in residential complexes, it was discerned that they are only present in recently developed complexes and are not being efficiently used. Office complexes like the Main Building fare better, but still show higher consumption than the norm.
As per preparatory studies done for Mumbai Development Plan for 2013-14 (sourced from MCGM), the actual per capita water consumption by an average citizen of Mumbai is 268 lcpd, far exceeded by IITB’s 358 lpcd
Why Do we Consume so Much?
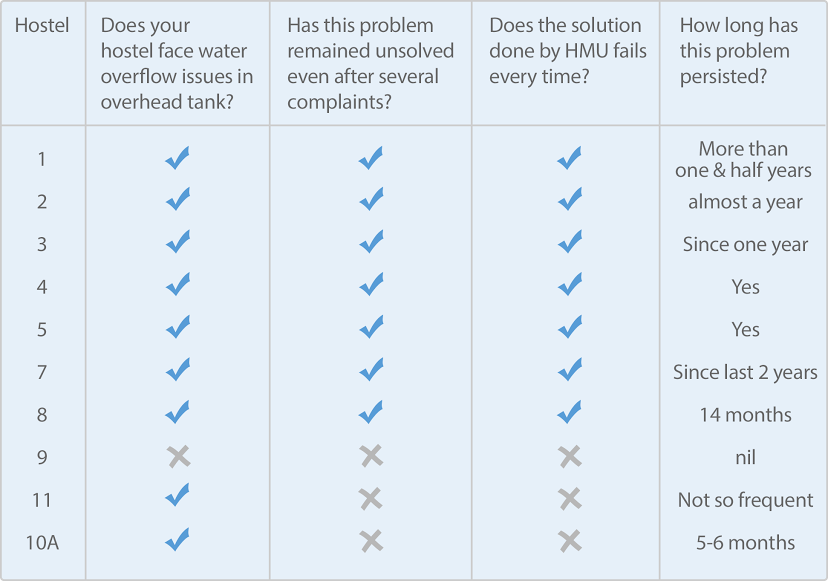
Here, we want highlight two important reasons for such high consumption: first, the institutional wastage of water through overflowing tanks and second, individual wastage of water due to consumer apathy.
A survey conducted by the previous GSHA Abbas Ali Bohra brought to notice the fact that nearly all our hostels had overflowing storage tanks for as long as two years (see the table attached). This has now been corrected temporarily, albeit in an ad-hoc manner, where valves are changed every three months. The main reason for this provisional arrangement is that the quality of valves being used is poor. These were downgraded after repeated pilfering of good quality valves.
As estimated from estate office data, the average litres of water consumed per person per day (LCPD) in the institute is approximately 358 litres.
To quote an instance, ex-GS of H1 Ratikanta Nayak asserts that after he reported the persistent and incessant water leakage in H1 tanks to the concerned authorities, only temporary rectifications were made, and the problem persisted till the end of April 2015. This amounts to more than one and a half years. Once students declared their intent to take this issue to the State Government, however, it was resolved within a month’s time.
The second issue is the indifference shown by campus residents. All too often, leaky taps in hostels are left unrepaired for weeks, on account of inaction by both general residents and authorities. For example, there exists a tap in H2 which has been slowly leaking for more than two years. A simulation done on a mildly leaking tap gave us wastage of 350 ml per minute, which when extrapolated gives a staggering figure of 500 litres of water wasted per day. Conservatively estimating 2 leaking faucets per hostel, this sums up to a flabbergasting figure of 17,000 litres of water wasted daily, by all hostels together. To put things in perspective, the 17,000 litres of water wasted every day is enough to satisfy the daily needs of 17 households of 4 people each, or for the sustenance of one person for about 24 years.
To put things in perspective, the 17,000 litres of water wasted every day is enough to satisfy the daily needs of 17 households of 4 people each, or for the sustenance of one person for about 24 years.
One underlying cause here is that water costs for students are highly subsidised. We pay Rs. 2500 per semester for both water and electricity. Considering our levels of consumption for these two resources, there is not enough monetary incentive for students to conserve water. The culture of wastage prevalent at IIT, which includes other important resources like food, can be ascribed as another reason.
The authorities have taken certain measures of late, but these seem too little considering the monstrosity of the problem. Proposals like an institute-wide water audit and use of level sensors in overhead tanks are still in the pipeline, with no specific timeline.
For example, there exists a tap in H2 which has been slowly leaking for more than two years. A simulation done on a mildly leaking tap gave us wastage of 350 ml per minute, which when extrapolated gives a staggering figure of 500 litres of water wasted per day.
Finally, we’d like to conclude by saying that a pro-active approach is needed by both authorities and general residents to curb incessant water wastage. The argument we wish to make, is not to increase fees so that students feel the bite of wastage, but to bring culprits to book and impose monetary fines to reign it in. Many institutes abroad perform surprise inspections to maintain checks on consumption levels. At the hostel level, we believe students must be held culpable. Councils need to ensure that reported cases are catered to within a specified time period and hold the concerned wings responsible for unreported leakages.
Recently, IIT Kanpur managed to bring down the energy consumption levels by 41% and water consumption levels by 70% from benchmarks set by the ‘Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA)’ body. Here are the few steps taken on campus on a relatively large scale to achieve these inspiring results:
- Existing trees preserved and protected on site.
- 62% reduction in building water consumption by use of low-flow fixtures.
- 50% reduction in landscape water consumption by minimizing lawn area and planting native species of trees and shrubs.
- Only 17% paved area to promote water percolation and reduce heat island effect.
- Rain water harvesting system designed for reuse and recharge.
- Waste water treated and reused for landscape water requirement
The details about the water supply network and consumption levels across different establishments in the institute were cited from a report published by Ms. Pooja Jain, a research coordinator in CTARA.
[Acknowledgment: This InsighT article was first published here.]
- Examination Without Invigilation – An experiment in trust - September 25, 2017
- Fragile Foundations: Infra @ IITB - October 17, 2016
